Cloud-Barista 👋
CB-Tumblebug (Multi-Cloud Infra Management)













What is CB-Tumblebug? ✨
CB-Tumblebug (CB-TB) is an advanced multi-cloud infrastructure management system that enables seamless provisioning, management, and orchestration of resources across multiple cloud service providers. Part of the Cloud-Barista project, CB-TB abstracts the complexity of multi-cloud environments into a unified, intuitive interface.
🎯 Key Capabilities
- 🌐 Multi-Cloud Orchestration: Manage AWS, Azure, GCP, Alibaba Cloud, and more from a single platform
- ⚡ Auto-provisioning: Intelligent resource recommendations and automated deployment
- 🔐 Secure Operations: Encrypted credential management and hybrid encryption protocols
- 🗺️ Visual Infrastructure Map: Interactive GUI for infrastructure visualization and management
- 🤖 AI-Powered Management: NEW! Control infrastructure using natural language via our MCP Server
📚 Documentation & Resources
📋 Development Status & Contributing Notes
🚧 Ongoing Development
CB-TB has not reached version 1.0 yet. We welcome any new suggestions, issues, opinions, and contributors!
Please note that the functionalities of Cloud-Barista are not yet stable or secure.
Be cautious if you plan to use the current release in a production environment.
If you encounter any difficulties using Cloud-Barista,
please let us know by opening an issue or joining the Cloud-Barista Slack.
🌍 Localization & Globalization
As an open-source project initiated by Korean members,
we aim to encourage participation from Korean contributors during the initial stages of this project.
Therefore, the CB-TB repository will accept the use of the Korean language in its early stages.
However, we hope this project will thrive regardless of contributors' countries in the long run.
To facilitate this, the maintainers recommend using English at least for
the titles of Issues, Pull Requests, and Commits, while accommodating local languages in the contents.
🌟 Featured Use Cases
🤖 NEW: AI-Powered Multi-Cloud Management
- Control CB-Tumblebug through AI assistants like Claude and VS Code
- Natural language interface for infrastructure provisioning and management using MCP (Model Context Protocol)
- Streamable HTTP transport for modern MCP compatibility
- 📖 MCP Server Guide | 🚀 Quick Start
🎮 GPU-Powered Multi-Cloud LLM Deployment

Table of Contents
- ⚡ Quick Start
- 🔧 Prerequisites
- 🚀 Installation & Setup
- 🌟 How to Use
- 🛠️ Development
- 🤝 Contributing
Quick Start ⚡
Get CB-Tumblebug running in under 5 minutes:
# 1. Automated setup (recommended for new users)
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug/main/scripts/set-tb.sh | bash
# 2. Start all services
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug
make up
# 3. Configure credentials (see detailed setup below)
./init/genCredential.sh
# Edit ~/.cloud-barista/credentials.yaml with your cloud credentials
./init/encCredential.sh
make init
# 4. Access services
# - API: http://localhost:1323/tumblebug/api
# - MapUI: http://localhost:1324
# - MCP Server: http://localhost:8000/mcp (if enabled)
💡 New to CB-Tumblebug? Follow the detailed setup guide below for comprehensive instructions.
Prerequisites 🔧
System Requirements
| Component |
Minimum Specification |
Recommended |
| OS |
Linux (Ubuntu 22.04+) |
Ubuntu 22.04 LTS |
| CPU |
4 cores |
8+ cores |
| Memory |
6 GiB |
16+ GiB |
| Storage |
20 GiB free space |
50+ GiB SSD |
| Example |
AWS c5a.xlarge |
AWS c5a.2xlarge |
⚠️ Performance Note: Lower specifications may cause initialization failures or performance degradation.
Required Software
- Docker & Docker Compose (latest stable)
- Go 1.25.0+ (for building from source)
- Git (for cloning repository)
Dependencies & Security
Installation & Setup 🚀
Option 1: Automated Setup (Recommended)
For new users on clean Linux systems:
# Download and run automated setup script
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug/main/scripts/set-tb.sh | bash
ℹ️ After the script finishes, you may need to log out and back in to activate Docker permissions and aliases.
If you'd prefer to install dependencies and clone the repository manually, follow the steps below. 👇
(1) Download CB-Tumblebug
-
Clone the CB-Tumblebug repository:
git clone https://github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug.git $HOME/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug
Optionally, you can register aliases for the CB-Tumblebug directory to simplify navigation:
echo "alias cdtb='cd $HOME/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug'" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "alias cdtbsrc='cd $HOME/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug/src'" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "alias cdtbtest='cd $HOME/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug/src/testclient/scripts'" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
-
Check Docker Compose Installation:
Ensure that Docker Engine and Docker Compose are installed on your system.
If not, you can use the following script to install them (note: this script is not intended for production environments):
# download and install docker with docker compose
curl -sSL get.docker.com | sh
# optional: add user to docker groupd
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
newgrp docker
# test the docker works
docker run hello-world
-
Start All Components Using Docker Compose:
To run all components, use the following command:
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug
docker compose up
This command will start all components as defined in the preconfigured docker-compose.yaml file. For configuration customization, please refer to the guide.
The following components will be started:
- ETCD: CB-Tumblebug KeyValue DB
- CB-Spider: a Cloud API controller
- CB-MapUI: a simple Map-based GUI web server
- CB-Tumblebug: the system with API server
- CB-Tumblebug MCP Server: AI assistant interface (if enabled)
- PostgreSQL: Specs and Images storage
- Traefik: Reverse proxy for secure access
Container Architecture Overview:
graph TB
subgraph "External Access"
User[👤 User]
AI[🤖 AI Assistant<br/>Claude/VS Code]
end
subgraph "Docker Compose Environment"
subgraph "Frontend & Interfaces"
UI[CB-MapUI<br/>:1324]
MCP[TB-MCP Server<br/>:8000]
Proxy[Traefik Proxy<br/>:80/:443]
end
subgraph "Backend Services"
TB[CB-Tumblebug<br/>:1323<br/>Multi-Cloud Management]
Spider[CB-Spider<br/>:1024<br/>Cloud API Abstraction]
ETCD[ETCD<br/>:2379<br/>Metadata Store]
PG[PostgreSQL<br/>:5432<br/>Specs/Images DB]
end
end
subgraph "Cloud Providers"
AWS[AWS]
Azure[Azure]
GCP[GCP]
Others[Others...]
end
%% User connections
User -->|HTTP/HTTPS| Proxy
User -->|HTTP| UI
User -->|HTTP| TB
AI -->|MCP HTTP| MCP
%% Proxy routing
Proxy -->|Route| UI
%% Internal service connections
UI -.->|API calls| TB
MCP -->|REST API| TB
TB -->|REST API| Spider
TB -->|gRPC| ETCD
TB -->|SQL| PG
%% Cloud connections
Spider -->|Cloud APIs| AWS
Spider -->|Cloud APIs| Azure
Spider -->|Cloud APIs| GCP
Spider -->|Cloud APIs| Others
%% Styling
classDef frontend fill:#e3f2fd,stroke:#1976d2
classDef backend fill:#f3e5f5,stroke:#7b1fa2
classDef storage fill:#e8f5e8,stroke:#388e3c
classDef cloud fill:#fff3e0,stroke:#f57c00
class UI,MCP,Proxy frontend
class TB,Spider,ETCD,PG backend
class AWS,Azure,GCP,Others cloud

After running the command, you should see output similar to the following:

Service Endpoints:
Note: Before using CB-Tumblebug, you need to initialize it.
To provisioning multi-cloud infrastructures with CB-TB, it is necessary to register the connection information (credentials) for clouds, as well as commonly used images and specifications.
-
Create credentials.yaml file and input your cloud credentials
-
Overview
credentials.yaml is a file that includes multiple credentials to use API of Clouds supported by CB-TB (AWS, GCP, AZURE, ALIBABA, etc.)- It should be located in the
~/.cloud-barista/ directory and securely managed.
- Refer to the
template.credentials.yaml for the template
-
Create credentials.yaml the file
Automatically generate the credentials.yaml file in the ~/.cloud-barista/ directory using the CB-TB script
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug
./init/genCredential.sh
-
Input credential data
Put credential data to ~/.cloud-barista/credentials.yaml (Reference: How to obtain a credential for each CSP)
### Cloud credentials for credential holders (default: admin)
credentialholder:
admin:
alibaba:
# ClientId(ClientId): client ID of the EIAM application
# Example: app_mkv7rgt4d7i4u7zqtzev2mxxxx
ClientId:
# ClientSecret(ClientSecret): client secret of the EIAM application
# Example: CSEHDcHcrUKHw1CuxkJEHPveWRXBGqVqRsxxxx
ClientSecret:
aws:
# ClientId(aws_access_key_id)
# ex: AKIASSSSSSSSSSS56DJH
ClientId:
# ClientSecret(aws_secret_access_key)
# ex: jrcy9y0Psejjfeosifj3/yxYcgadklwihjdljMIQ0
ClientSecret:
...
-
Encrypt credentials.yaml into credentials.yaml.enc
To protect sensitive information, credentials.yaml is not used directly. Instead, it must be encrypted using encCredential.sh. The encrypted file credentials.yaml.enc is then used by init.py. This approach ensures that sensitive credentials are not stored in plain text.
-
Encrypting Credentials
init/encCredential.sh
When executing the script, you have two options: 1) enter your password or 2) let the system generate a random passkey.
Option 1: Entering your password:

Option 2: Letting the system generate a random passkey, which MUST be securely stored in a safe location:

If you need to update your credentials, decrypt the encrypted file using decCredential.sh, make the necessary changes to credentials.yaml, and then re-encrypt it.
-
Decrypting Credentials
init/decCredential.sh
Option 1: If encrypted using option 1, please use the same password to decrypt the file:

Option 2: If encrypted using option 2, enter the passkey to decrypt the file:

-
(INIT) Register all multi-cloud connection information and common resources
-
How to register
Refer to README.md for init.py, and execute the init.py script by the init.sh. (enter 'y' for confirmation prompts)
init.sh --help will show the available options.
You can also simply use the make init command as follows:
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug
make init
-
The credentials in ~/.cloud-barista/credentials.yaml.enc (encrypted file from the credentials.yaml) will be automatically registered (all CSP and region information recorded in cloudinfo.yaml will be automatically registered in the system)
- Note: You can check the latest regions and zones of CSP using
update-cloudinfo.py and review the file for updates. (contributions to updates are welcome)
-
Common images and specifications recorded in the cloudimage.csv and cloudspec.csv files in the assets directory will be automatically registered.
-
init.py will apply the hybrid encryption for secure transmission of credentials
- Retrieve RSA Public Key: Use the
/credential/publicKey API to get the public key.
- Encrypt Credentials: Encrypt credentials with a randomly generated
AES key, then encrypt the AES key with the RSA public key.
- Transmit Encrypted Data: Send
the encrypted credentials and AES key to the server. The server decrypts the AES key and uses it to decrypt the credentials.
This method ensures your credentials are securely transmitted and protected during registration. See init.py for a Python implementation.
In detail, check out Secure Credential Registration Guide (How to use the credential APIs)
(4) Shutting down and Version Upgrade
-
Shutting down CB-TB and related components
-
Stop all containers by ctrl + c or type the command docker compose stop / docker compose down / make down
(When a shutdown event occurs to CB-TB, the system will be shutting down gracefully: API requests that can be processed within 10 seconds will be completed)

-
In case of cleanup is needed due to internal system errors
-
Upgrading the CB-TB & CB-Spider versions
The following cleanup steps are unnecessary if you clearly understand the impact of the upgrade
How to Use CB-TB Features 🌟
- 🤖 Using CB-TB MCP Server (AI Assistant Interface) (NEW!)
- Using CB-TB MapUI (recommended)
- Using CB-TB REST API (recommended)
Using CB-TB MCP Server
🚀 NEW: Control CB-Tumblebug with AI assistants like Claude!
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server enables natural language interaction with CB-Tumblebug through AI assistants:
- 🧠 AI-Powered Infrastructure Management: Deploy and manage multi-cloud resources using natural language commands
- 🔗 Seamless Integration: Works with Claude Desktop (via proxy), VS Code (direct), and other MCP-compatible clients
- 📡 Modern Protocol: Uses Streamable HTTP transport (current MCP standard)
- ⚡ Quick Start: Enable with
make up and uncomment MCP service in docker-compose.yaml
# Enable MCP Server (Proof of Concept)
# 1. Uncomment cb-tumblebug-mcp-server in docker-compose.yaml
# 2. Launch with Docker Compose
make up
# Access MCP server at http://localhost:8000/mcp
📖 Complete MCP Server Guide →
⚠️ Note: MCP Server is a Proof of Concept. Review code thoroughly before production use.
Using CB-TB MapUI 🗺️
Visual Infrastructure Management with Interactive Maps
CB-MapUI provides an intuitive, map-based interface for managing multi-cloud infrastructure:
- 🗺️ Geographic Visualization: See your infrastructure deployed across the globe
- 📊 Real-time Monitoring: Monitor resource status and performance
- 🎮 Interactive Control: Create, manage, and control resources visually
- 🌐 Multi-Cloud View: Unified view across all cloud providers
# Access CB-MapUI (auto-started with Docker Compose)
open http://localhost:1324
# Or run standalone MapUI container
./scripts/runMapUI.sh
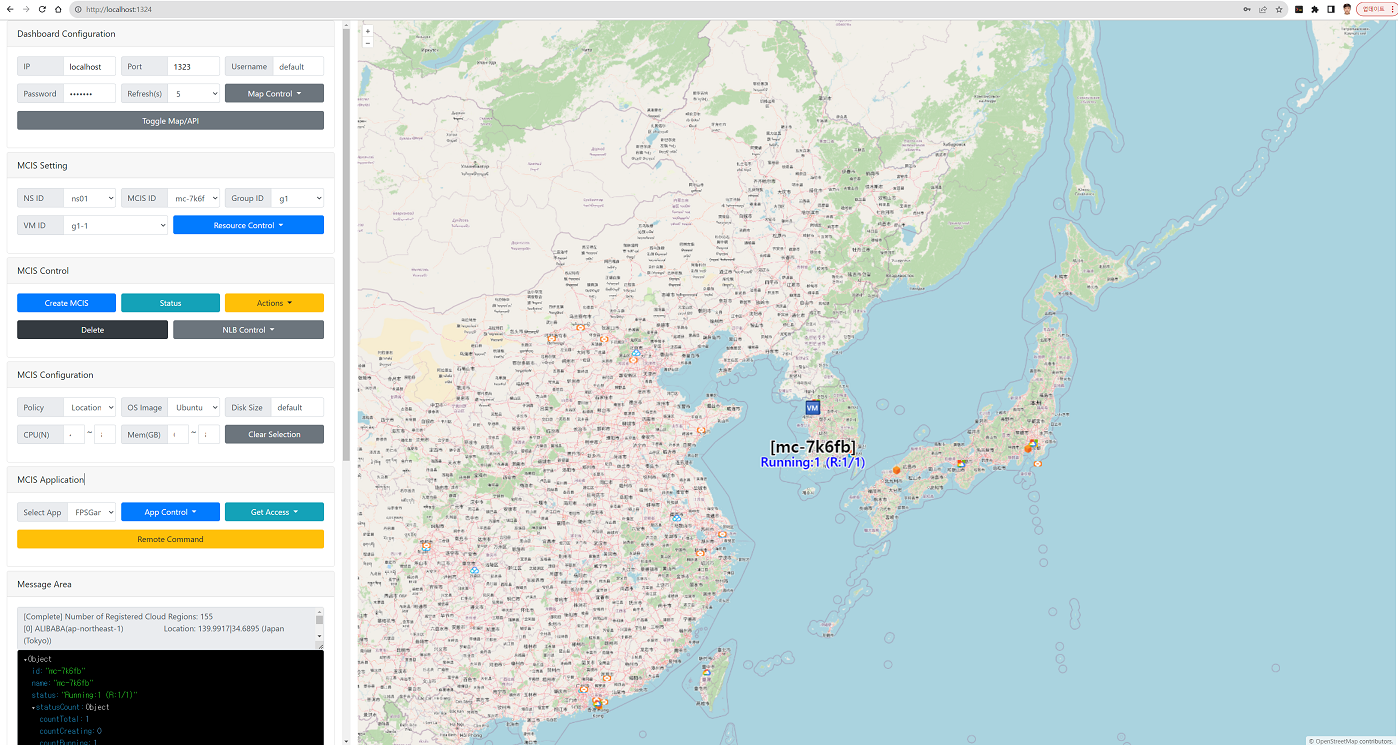
Features:
- Drag-and-drop resource creation
- Real-time infrastructure mapping
- Cross-cloud resource relationships
- Performance metrics overlay
📖 Learn More: CB-MapUI Repository
Using CB-TB REST API 🔌
Programmatic Multi-Cloud Infrastructure Management
CB-Tumblebug provides a comprehensive REST API for automated infrastructure management:
🌐 API Dashboard & Documentation
🔐 Authentication
CB-TB uses Basic Authentication (development phase - not production-ready):
# Include base64 encoded credentials in request headers
Authorization: Basic <base64(username:password)>
🚀 Quick Infrastructure Creation
Following the Quick MCI Creation Guide:
# 1. Create VM specification
curl -X POST "http://localhost:1323/tumblebug/ns/default/resources/spec" \
-H "Authorization: Basic <credentials>" \
-d '{"name": "web-spec", "connectionName": "aws-ap-northeast-2"}'
# 2. Create VM image
curl -X POST "http://localhost:1323/tumblebug/ns/default/resources/image" \
-H "Authorization: Basic <credentials>" \
-d '{"name": "ubuntu-image", "connectionName": "aws-ap-northeast-2"}'
# 3. Create Multi-Cloud Infrastructure
curl -X POST "http://localhost:1323/tumblebug/ns/default/mci" \
-H "Authorization: Basic <credentials>" \
-d @mci-config.json
🛠️ Core API Categories
- Infrastructure Resources: VM specs, images, networks, security groups
- Multi-Cloud Infrastructure (MCI): Provision and manage distributed infrastructure
- Monitoring & Control: Performance metrics, scaling, lifecycle management
- Credentials & Connections: Secure cloud provider configuration
- Create access key object
- Create, view, control, execute remote commands, shut down, and delete MCI using the MCI(multi-cloud infrastructure service) management APIs
- CB-TB optimal and dynamic provisioning
Multi-Cloud Infrastructure Use Cases
Deploying an MCI Xonotic (3D FPS) Game Server
Distributed Deployment of MCI Weave Scope Cluster Monitoring
Deploying MCI Jitsi Video Conferencing
Automatic Configuration of MCI Ansible Execution Environment
How to Build 🛠️
(1) Setup Prerequisites
(2) Build and Run CB-Tumblebug
(2-1) Option 1: Run CB-Tumblebug with Docker Compose (Recommended)
-
Run Docker Compose with the build option
To build the current CB-Tumblebug source code into a container image and run it along with the other containers, use the following command:
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug
sudo DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker compose up --build
This command will automatically build the CB-Tumblebug from the local source code
and start it within a Docker container, along with any other necessary services as defined in the docker-compose.yml file. DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 setting is used to speed up the build by using the go build cache technique.
(2-2) Option 2: Run CB-Tumblebug from the Makefile
-
Build the Golang source code using the Makefile
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug/src
make
All dependencies will be downloaded automatically by Go.
The initial build will take some time, but subsequent builds will be faster by the Go build cache.
Note To update the Swagger API documentation, run make swag
-
Set environment variables required to run CB-TB (in another tab)
- Check and configure the contents of
cb-tumblebug/conf/setup.env (CB-TB environment variables, modify as needed)
-
Execute the built cb-tumblebug binary by using make run
cd ~/go/src/github.com/cloud-barista/cb-tumblebug/src
make run
How to Contribute 🙏
CB-TB welcomes improvements from both new and experienced contributors!
Check out CONTRIBUTING.
Contributors ✨
Thanks goes to these wonderful people (emoji key):
License

 Directories
¶
Directories
¶










