koko: Container connector (for chaining)



What is 'koko'?
koko is a simple tool which connects between Docker containers/linux netns processes with veth devices/vxlan
of linux kernel. Using koko, you can simply make point-to-point connection for containers without linux bridges.
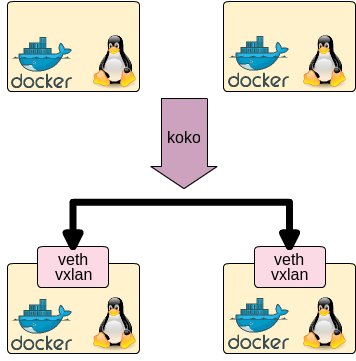
Support Container Type and Interfaces
koko supports following container:
- Docker
- Linux netns namespace (i.e. 'ip netns' or see 'man ip-netns' for its detail)
koko supports following linux interface to connect above:
- veth: Virtual Ethernet Interface
- vxlan: Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network
Get Releases
See releases page.
Build Requirements
Build
koko is written in go, so following commands makes koko single binary. Build and put it in your container host.
git clone https://github.com/redhat-nfvpe/koko.git
cd koko
go get
go build
Syntax
koko takes two arguments: two endpoints of container and koko connects both.
koko supports veth for two containers in one host and vxlan for two containers in separate host.
Connecting containers in container host using veth
./koko {-c <linkname> |
-d <container>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] |
-n <netns name>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...]|
-p <pid>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...]}
{-d <container>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] |
-n <netns name>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...]|
-p <pid>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...]}
Connecting containers using vxlan (interconnecting container hosts)
Connecting containers which are in separate hosts with vxlan. Following command makes vxlan interface
and put this interface into given container with/without IP address.
./koko {-c <linkname> |
-d <container>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] |
-n <netns name>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...]|
-p <pid>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] }
-x <parent interface>:<remote endpoint IP addr>:<vxlan id>
Connecting containers using VLAN
Connecting containers which are in separate hosts with vlan. Following command makes vlan interface
and put this interface into given container with/without IP address.
./koko {-c <linkname> |
-d <container>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] |
-n <netns name>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...]|
-p <pid>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] }
-V <parent interface>:<vlan id>
Connecting containers using macvlan
Connecting containers which are in separate hosts with macvlan. Following command makes macvlan interface
and put this interface into given container with/without IP address.
./koko {-c <linkname> |
-d <container>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] |
-n <netns name>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...]|
-p <pid>,<linkname>[,<IP addr>/<prefixlen>,...] }
-M <parent interface>:<macvlan mode, {default|private|vepa|bridge|passthru}>
Delete link in containers
koko -D and koko -N deletes veth interface or vxlan interface. In case of veth, peering interface is also
removed in this command.
./koko {-D <container>,<linkname> | -N <netns name>,<linkname> }
Command option summary
-c is to create veth and put it in current namespace.-d is to create interface and put it in docker container namespace-D is to delete interface of docker container namespace-n is to create interface and put it in linux netns namespace-N is to delete interface of linux netns namespace-p is to create interface and put it in pid's netns namespace-P is to delete interface of pid's netns namespace-X is to create vxlan interface-V is to create vlan interface-M is to create macvlan interface-h is to show help-v is to show version
Printing help
./koko -h
Usage
Please see Examples in Wiki.
Example
# connect between docker containers with IPv4 address
sudo ./koko -d centos1,link1,192.168.1.1/24 -d centos2,link2,192.168.1.2/24
# connect between docker containers with IPv6 address
sudo ./koko -d centos1,link1,2001:DB8::1/64 -d centos2,link2,2001:DB8::2/64
# connect between docker containers with IPv4/IPv6 address
sudo ./koko -d centos1,link1,192.168.1.1/24,2001:DB8::1/64 -d centos2,link2,192.168.1.2/24,2001:DB8::2/64
# connect between netns namespaces
sudo ./koko -n testns1,link1,192.168.1.1/24 -n testns2,link2,192.168.1.2/24
# connect between docker container and netns namespace
sudo ./koko -d centos1,link1,192.168.1.1/24 -n testns2,link2,192.168.1.2/24
# create vxlan interface and put it into docker container
sudo ./koko -d centos1,link1,192.168.1.1/24 -x eth1,10.1.1.1,1
Todo
Authors
- Tomofumi Hayashi (s1061123)
- Doug Smith (dougbtv)