srctx: source context
A lib for source context analysis based on LSIF.
| Name |
Status |
| Latest Version |
 |
| Unit Tests |
 |
| Code Coverage |
 |
| Code Style |
 |
What's LSIF?
LSIF is a standard format for persisted code analyzer output.
Today, several companies are working to support its growth, including Sourcegraph and GitHub/Microsoft.
The LSIF defines a standard format for language servers or other programming tools to emit their knowledge about a code workspace.
https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/overviews/lsif/overview/
This lib processes LSIF file into graphs then you can apply some analysis on them.
This lib originally was designed for monitoring the influence of each commits.
Usecase with git diff
With the raw diff, we can only get something like:
@@ -19,6 +20,7 @@ func AddDiffCmd(app *cli.App) {
var lsifZip string
var outputJson string
var outputCsv string
+ var outputDot string
diffCmd := &cli.Command{
Name: "diff",
:
If we need to know the impact of these line changes on the entire repository, we can only rely on manual reading of the code to evaluate.
With this lib developers can know exactly what happened in every lines of your code. Such as definition, reference. For example, get all the references happened in a specific line:
vertices, _ := sourceContext.RefsByLine(path, eachLine)
log.Debugf("path %s line %d affected %d vertexes", path, eachLine, len(vertices))
Some "dangerous" line changes can be found automatically.
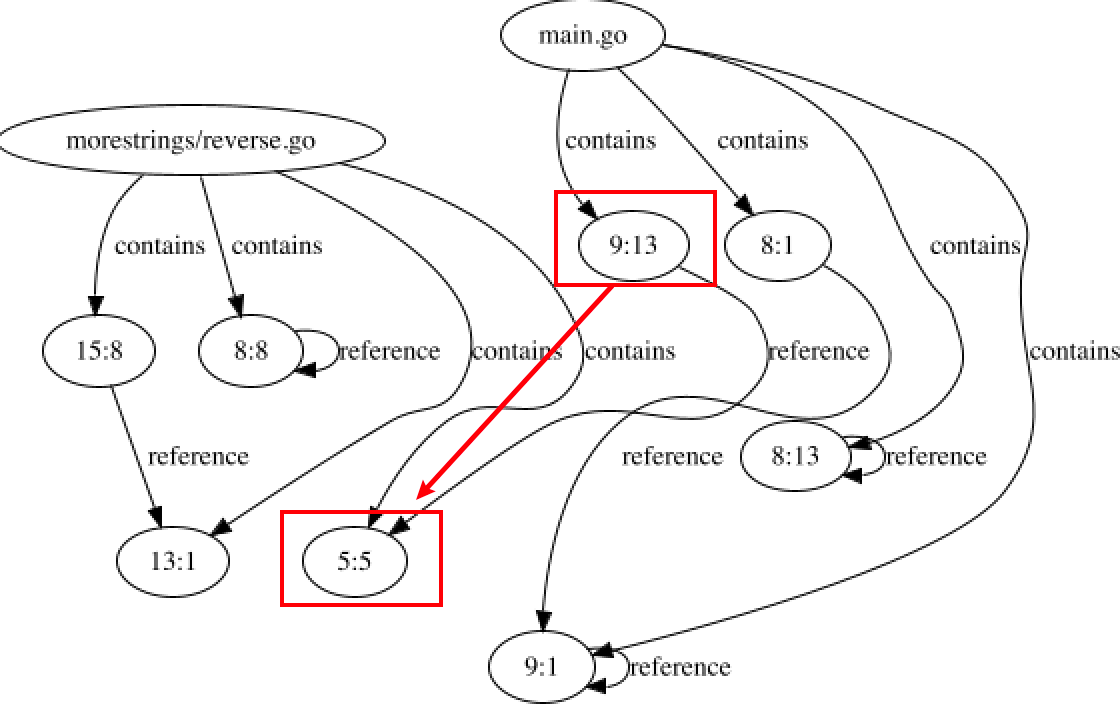
We hope to utilize the powerful indexing capabilities of LSIF to quantify and evaluate the impact of text changes on the repository, reducing the mental burden on developers.
Usage
Usage as Lib
yourLsif := "../parser/lsif/testdata/dump.lsif.zip"
sourceContext, _ := parser.FromLsifFile(yourLsif)
// all files?
files := sourceContext.Files()
log.Infof("files in lsif: %d", len(files))
// search definition in a specific file
defs, _ := sourceContext.DefsByFileName(files[0])
log.Infof("there are %d def happend in %s", len(defs), files[0])
for _, eachDef := range defs {
log.Infof("happened in %d:%d", eachDef.LineNumber(), eachDef.Range.Character)
}
// or specific line?
_, _ = sourceContext.DefsByLine(files[0], 1)
// get all the references of a definition
refs, err := sourceContext.RefsByDefId(defs[0].Id())
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
log.Infof("there are %d refs", len(refs))
for _, eachRef := range refs {
log.Infof("happened in file %s %d:%d",
sourceContext.FileName(eachRef.FileId),
eachRef.LineNumber(),
eachRef.Range.Character)
}
Or see cmd/srctx/cmd_diff.go for a real example with git diff.
Usage as Cli
A full example can be found in our CI: https://github.com/williamfzc/srctx/blob/f2f236872914674d3fdc8c08b0d35e89096a8ff2/.github/workflows/ci.yml#L25
1. Generate LSIF file
https://lsif.dev/
LSIF is a standard format for persisted code analyzer output.
Today, several companies are working to support its growth, including Sourcegraph and GitHub/Microsoft.
You can easily find an existed tool for generating LSIF file for your repo.
You will get a dump.lsif file after that.
2. Run srctx
Download our prebuilt binaries from release page.
./srctx diff --lsif dump.lsif --outputCsv output.csv
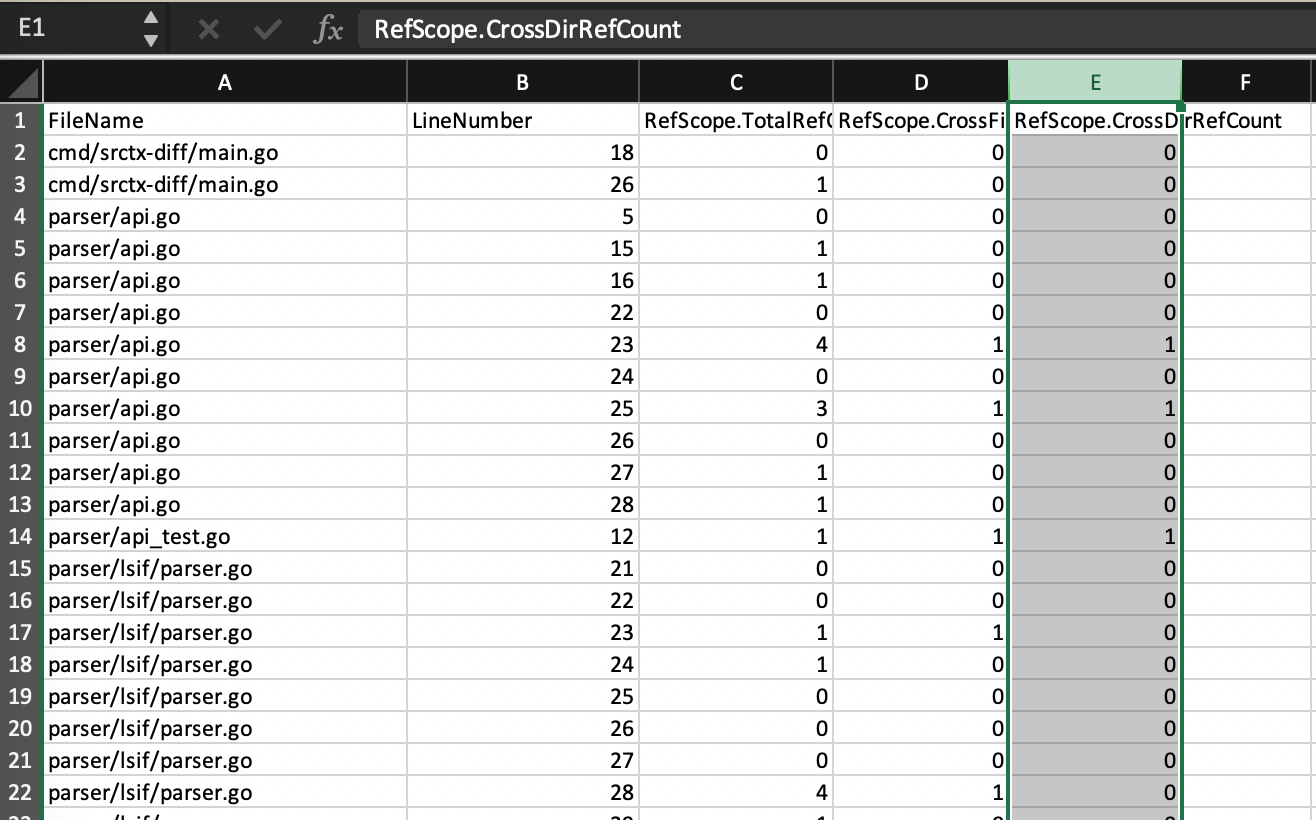
You can see every edited lines and their impacts. Currently we provided:
- total referenced
- referenced out of current files
- referenced out of current dir
Roadmap
- keep more data from LSIF
- combination with AIGC
Contribution
Issues and PRs are always welcome.
References
License
Apache 2.0