sponge

sponge is a microservices framework for quickly creating http or grpc code. Generate codes config, ecode, model, dao, handler, router, http, proto, service, grpc from SQL DDL, these codes can be combined into complete services (similar to how a broken sponge cell can automatically reorganize into a new sponge).
sponge framework diagram:
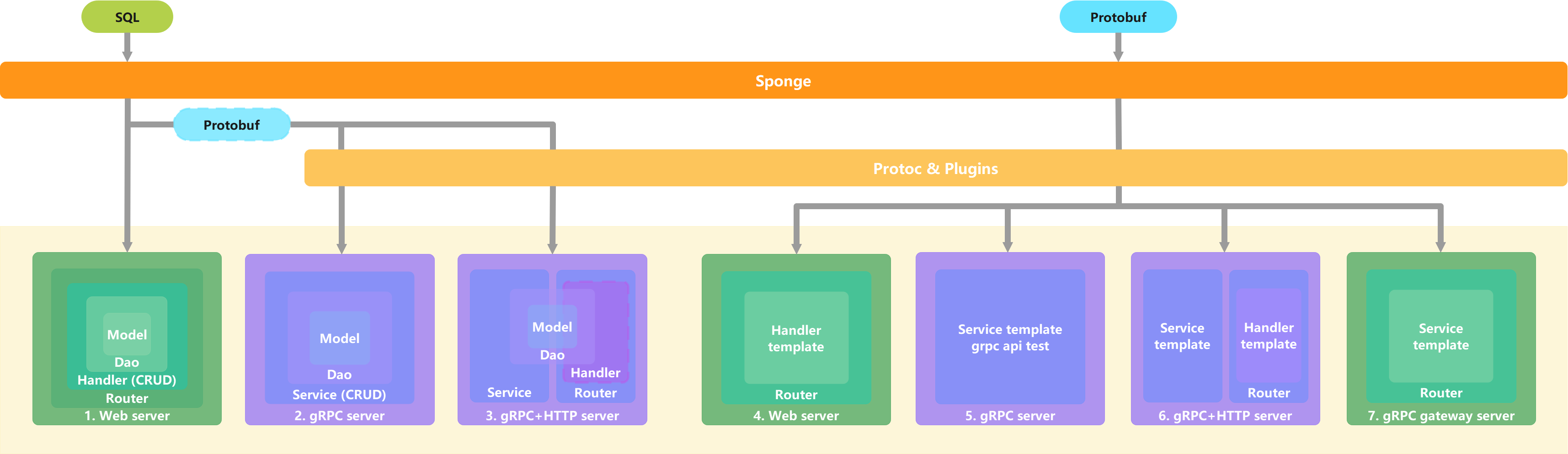
microservices framework diagram:
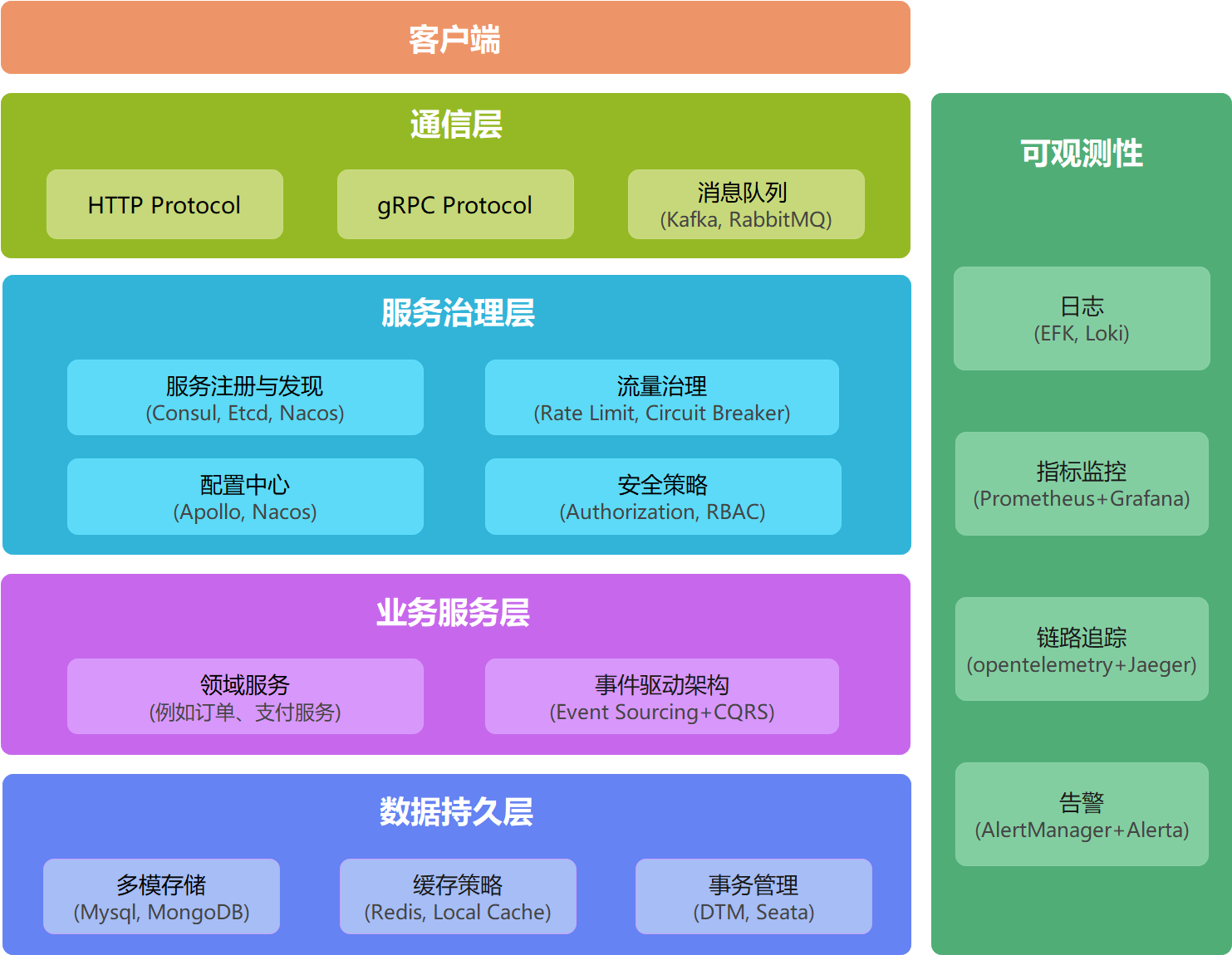
Features :
The directory structure follows golang-standards/project-layout.
.
├── api # Grpc's proto file and corresponding code
├── assets # Other assets used with the repository (images, logos, etc.)
├── build # Packaging and continuous integration
├── cmd # The application's directory
├── configs # Directory of configuration files
├── deployments # IaaS, PaaS, system and container orchestration deployment configurations and templates
├─ docs # Design documentation and interface documentation
├── internal # Private application and library code
│ ├── cache # Business wrapper-based cache
│ ├── config # Go struct for config file mapping
│ ├── dao # Data access
│ ├── ecode # Custom business error codes
│ ├── handler # Business function implementation for http
│ ├── model # Database model
│ ├── routers # Http routing
│ ├── server # Service entry, including http and grpc servers
│ ├── service # Business function implementation for grpc
│ └── types # Request and response types for http
├── pkg # library code that external applications can use
├── scripts # Scripts for performing various build, install, analysis, etc. operations
├── test # Additional external test applications and test data
└── third_party # External helpers, forked code and other third party tools
The development specification follows the Uber Go Language Coding Specification.
Quick start
Install
Add $GOROOT/bin to the system path.
go install github.com/zhufuyi/sponge/cmd/sponge@latest
sponge update
Quickly create a http project
Creating a new http server
(1) Generate http server code
sponge http \
--module-name=account \
--server-name=account \
--project-name=account \
--repo-addr=zhufuyi \
--db-dsn=root:123456@(127.0.0.1:3306)/test \
--db-table=student
(2) If using the default configuration, skip this step. Modify the configuration file configs/.yml
- If the field
cacheType is redis, the redis address must be set.
- If the field
enableTracing is true, the jaeger address must be set.
- If the field
enableRegistryDiscovery is true, the configuration of the corresponding type of registryDiscoveryType must be set.
(3) Generate swagger documentation
make docs
(4) Start up the server
Way 1: Run locally in the binary
make run
Copy http://localhost:8080/swagger/index.html to your browser and test the api interface.
Way 2: Run in docker. Prerequisite: docker and docker-compose are already installed.
# Build the docker image
make docker-image
# Start the service
make deploy-docker
# Check the status of the service, if it is healthy, it started successfully
cd deployments/docker-compose
docker-compose ps
Way 3: Run in k8s. Prerequisite: docker and kubectl are already installed.
# Build the image
make image-build REPO_HOST=zhufuyi TAG=latest
# Push the image to the remote image repository and delete the local image after a successful upload
make image-push REPO_HOST=zhufuyi TAG=latest
# Deploy to k8s
kubectl apply -f deployments/kubernetes/*namespace.yml
kubectl apply -f deployments/kubernetes/
make deploy-k8s
# Check the status of the service
kubectl get -f account-deployment.yml
You can also use Jenkins to automatically build deployments to k8s.
Creating a new handler
add a new handler to an existing http server.
sponge handler \
--module-name=account \
--db-dsn=root:123456@(127.0.0.1:3306)/test \
--db-table=teacher \
--out=./account
Start up the server
make docs && make run
Copy http://localhost:8080/swagger/index.html to your browser and test the api interface.
Quick create a grpc project
Creating a new grpc server
(1) Generate grpc server code
sponge grpc \
--module-name=account \
--server-name=account \
--project-name=account \
--repo-addr=zhufuyi \
--db-dsn=root:123456@(127.0.0.1:3306)/test \
--db-table=student
(2) If using the default configuration, skip this step. Modify the configuration file configs/.yml
- If the field
cacheType is redis, the redis address must be set.
- If the field
enableTracing is true, the jaeger address must be set.
- If the field
enableRegistryDiscovery is true, the configuration of the corresponding type of registryDiscoveryType must be set.
(3) Generating grpc code
make proto
(4) Start up the server
Way 1: Run locally in the binary
make run
Use IDE to open the file internal/service/<table name>_client_test.go to test the api interface of grpc, you can copy the pressure test report to your browser to view it. Or use the go test command to execute the test cases.
Way 2: Run in docker
# Build the docker image
make docker-image
# Start the service
make deploy-docker
# Check the status of the service, if it is healthy, it started successfully
cd deployments/docker-compose
docker-compose ps
Way 3: Run in k8s
# Build the image
make image-build REPO_HOST=zhufuyi TAG=latest
# Push the image to the remote image repository and delete the local image after a successful upload
make image-push REPO_HOST=zhufuyi TAG=latest
# Deploy to k8s
kubectl apply -f deployments/kubernetes/*namespace.yml
kubectl apply -f deployments/kubernetes/
make deploy-k8s
# Check the status of the service
kubectl get -f deployments/kubernetes/account-deployment.yml
You can also use Jenkins to automatically build deployments to k8s.
Creating a new service
add a new service to an existing grpc server.
sponge service \
--module-name=account \
--server-name=account \
--db-dsn=root:123456@(127.0.0.1:3306)/test \
--db-table=teacher \
--out=./account
Start up the server
make proto && make run
Use IDE to open the file internal/service/<table name>_client_test.go to test the api interface of grpc.
License
See the LICENSE file for licensing information.
 Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶
 Directories
¶
Directories
¶



